

Note the way precipitation reactions appear as molecular equations and net ionic equations. Here are common examples of precipitation reactions. When the particles become large enough, they precipitate or fall out of solution. Initially, nucleation may lead to the formation of a suspension of tiny solid particles in liquid. Other nucleation sites include solid impurities in the solution and gas bubbles. During nucleation, tiny particles adhere to each other and to surface imperfections on the container. In all cases, precipitation starts with nucleation. The other ways of forming precipitates are more processes than reactions. Adding ions is another option, driving a compound toward solidification.Ī double replacement reaction that forms a precipitate is a precipitation reaction.
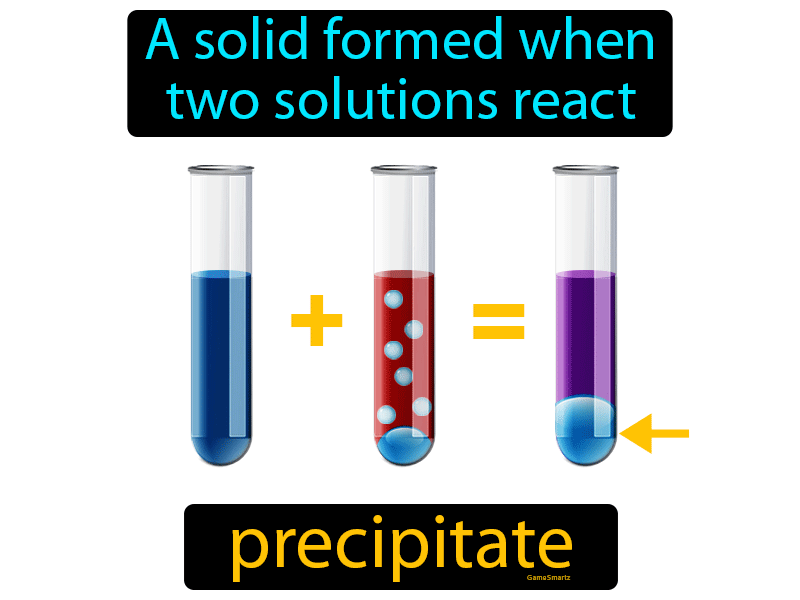
Double replacement reaction: Often, precipitation results from a double replacement reaction between two aqueous solutions.Precipitation results from the concentration of a chemical exceeding its solubility. Down arrow: Otherwise, a down arrow (↓) after the name or formula indicates a precipitate.State of matter symbol: Including the symbol (s) following a chemical formula means the product is a solid.There are two common ways to indicate precipitation in a chemical reaction. The remaining solution is the supernate or supernatant. In chemistry, a precipitation reaction is a chemical reaction between two dissolved substances that forms one or more solid products.

This entry was posted on Augby Anne Helmenstine (updated on February 3, 2022)Ī precipitation reaction occurs when two dissolved substances react and form one or more solid products.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
